Catalytic Ozone Technology for Water Treatment Summary of 3 Commonly Used Catalysts
Ozone catalytic oxidation technology is an advanced oxidation technology based on ozone, which combines the strong oxidizing property of ozone and the adsorption and catalytic property of catalyst, and can solve the problem of incomplete degradation of organic matter more effectively.
Ozone catalytic oxidation technology is divided into homogeneous ozone catalytic oxidation technology and multiphase ozone catalytic oxidation technology according to the phase state of the catalyst. In homogeneous ozone catalytic oxidation technology, the catalyst is uniformly distributed and has high catalytic activity, and the mechanism of action is clear and easy to study and grasp. However, its shortcomings are also obvious, the catalyst miscible in water, resulting in its easy to lose, not easy to recover and produce secondary pollution, high operating costs, increasing the cost of water treatment. Multi-phase ozone catalytic oxidation technology using solid catalysts at atmospheric pressure to accelerate the oxidation reaction of the liquid phase (or gas phase), the catalyst exists in solid state, easy to separate from the water, less secondary pollution, and simplify the treatment process, which is increasingly attracting widespread attention.
For ozone catalytic oxidation technology technology, the selection of solid catalysts is the key to the efficient oxidation effectiveness of the technology. It is found that multiphase catalysts have three main roles:
First, adsorption of organic matter, for those catalysts with relatively large adsorption capacity, when water comes into contact with the catalyst, the organic matter in the water is first adsorbed on the surface of these catalysts, forming surface chelates with affinity, making ozone oxidation more efficient.
Secondly, catalytic activation of ozone molecules, this kind of catalyst has high efficiency catalytic activity, can effectively catalytic activation of ozone molecules, ozone molecules in the role of this kind of catalyst is easy to decompose and produce such as hydroxyl radicals and other highly oxidizing radicals, thus improving the efficiency of ozone oxidation.
Third, adsorption and activation synergism, this type of catalyst not only can efficiently adsorb organic pollutants in water, but also can catalyze the activation of ozone molecules, generating highly oxidizing free radicals, on the surface of this type of catalyst, the adsorption of organic pollutants and oxidants activation synergism can achieve better catalytic ozone oxidation effect.

The catalysts involved in multiphase ozone catalytic oxidation technology are mainly metal oxides (Al2O3, TiO2, MnO2, etc.), metal or metal oxides loaded on the carrier (CuTiO2, CuAl2O3, TiO2AlO3, etc.) and pore materials with large specific surface area. The catalytic activity of these catalysts is mainly characterized by the catalytic decomposition of ozone and the promotion of hydroxyl radicals. The efficiency of the ozone catalytic oxidation process depends mainly on the catalyst and its surface properties, the pH of the solution, which can affect the nature of the active sites on the surface of the catalyst and the ozone decomposition reaction in solution.
1. (loaded) metal catalysts prepared in a certain way can induce the decomposition of ozone in water and produce free radicals with very strong oxidizing properties, thus significantly improving their decomposition effect on highly stable organic matter in water. Many metals can be used to catalyze the ozone oxidation process, such as titanium, copper, zinc, iron, nickel, manganese and so on.
2. Metal oxides metal oxides can directly affect the rational choice of catalytic reaction mechanism and efficiency. Generally, the hydroxyl group on the surface of metal oxides is the active site of the catalytic reaction, which adsorbs anions and cations from water by releasing protons and hydroxyl groups into water and undergoes an ion-exchange reaction, resulting in the formation of a Bronsted acidic site, which is usually considered to be the catalytic center of the metal oxides. Several metal oxide catalysts, such as TiO2, Al2O3, and MnO2, which have been widely studied, are described in detail below.
(1). Titanium dioxide TiO2TiO2 is generally used as a photocatalytic reaction, but it is also effective in ozone-catalyzed oxidation of organic matter in water, either as a catalyst for the ozonation reaction alone or as a co-catalyst for ozonation together with UV light.Beltran et al. investigated the effect of catalytic ozonation for the degradation of oxalic acid using TiO2 powder as a catalyst. Compared with the ozone oxidation system alone, the removal rate and mineralization degree of oxalic acid by multiphase catalytic ozonation were greatly improved.
(2). Alumina Al2O3Al2O3 is usually used as a carrier for catalysts, but some researchers have found that it also has some ability to catalyze ozonation.Ni and Chen showed that the presence of y-Al2O3 increased the organic carbon removal of 2-chlorophenol from 21% to 43% with ozone oxidation alone, and that ozone depletion was only half of that with ozonation alone. There was no significant change in the removal effect after three consecutive uses of the catalyst.
(3). Manganese dioxide MnO2 Among all transition metal oxides, MnO2 is considered to exhibit the best catalytic activity and can effectively catalyze the degradation of the largest number of organic species. In recent years, the emergence of nanomaterials has provided new opportunities for the development of new and efficient catalytic materials for ozonation, and the use of nanomaterials has improved the catalytic efficiency of the catalysts compared to conventional bulk phase catalysts. The investigation of transition metal oxide nanomaterials for catalytic applications has been reported in many literatures. In catalytic ozonation, some nanocatalysts with transition metal oxides as active components, such as CO3O4, Fe2O.

3. TiO ZnO and so on have achieved better catalytic effect.3 Activated Carbon Activated carbon is a carbonaceous material consisting of a mixture of tiny crystalline and non-crystalline parts, and the surface of activated carbon contains a large number of acidic or basic groups, and the presence of these acidic or basic groups, especially hydroxyl and phenolic hydroxyl, makes the activated carbon not only adsorption ability but also catalytic ability. During the ozone/activated carbon synergistic process, ozone is accelerated into hydroxyl radicals by the adsorption of activated carbon, thus improving the oxidation efficiency. The difference between activated carbon as a catalyst and metal oxide as a catalyst for catalytic ozonation is the different decomposition mechanism of ozone: the Lewis base on the surface of activated carbon plays the main role; while the Lewis acid on the surface of the metal oxide is the active point of the catalytic process. In addition, for the activated carbon catalytic system, the adsorption property of the activated carbon surface plays a greater role, so the ozonation degradation efficiency is greatly affected by the acidity and alkalinity of the medium. Currently, there is a large body of literature describing the mechanism of multiphase ozone-catalyzed oxidation technology. Three possible mechanisms are generally recognized:
(1). It is believed that organic matter is chemisorbed onto the surface of the catalyst, forming surface chelates with some nucleophilicity, with which ozone or hydroxyl radicals then undergo an oxidation reaction, forming intermediates that can be further oxidized on the surface, or may desorb into solution to be further oxidized, as shown in Fig. 1. The catalytic oxidation system of some catalysts with relatively large adsorption capacity tends to follow this mechanism.
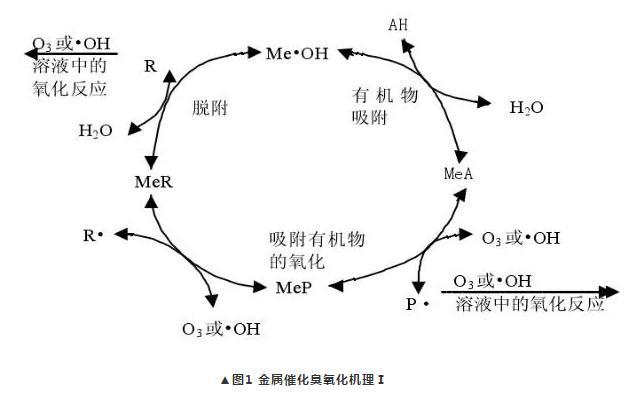
(2). The catalyst not only adsorbs organic matter, but also directly reacts with ozone in a redox reaction, producing oxidized state metals and hydroxyl radicals that can directly oxidize organic matter, as shown in Figure 2.
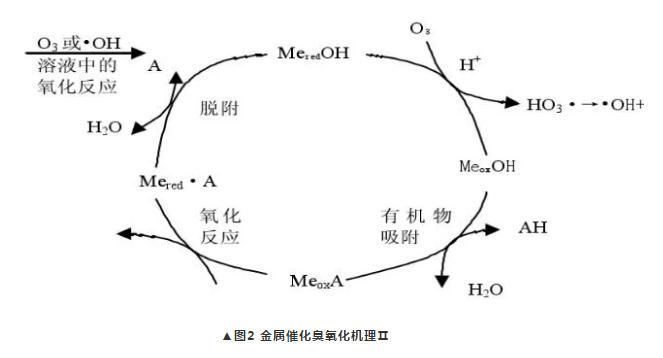
(3). Catalysts catalyze the decomposition of ozone to produce a more reactive oxidant, which reacts with non-chemically adsorbed organic molecules.






